Quick Links
Whether you are looking at a space documentary, reading a geek-to-song space article, or just trying to fix your head, which is present around us, learning the meaning of these major words will help you understand what is in the universe.
1
Universe
The universe is the entire physical universe, which is seen as a systematic, systematic whole instead of random, chaotic collection of matter.
It includes space, time, substance, energy and all the natural laws that have controlled them in the past, now controlling them, and will rule them in the future.

Connected
5 biggest cosmic secrets that scientists are still trying to solve
We can never have satisfactory answers.
2
Case
The substance (and antimatter) is anything in the space that has mass and volume and the space is occupied.
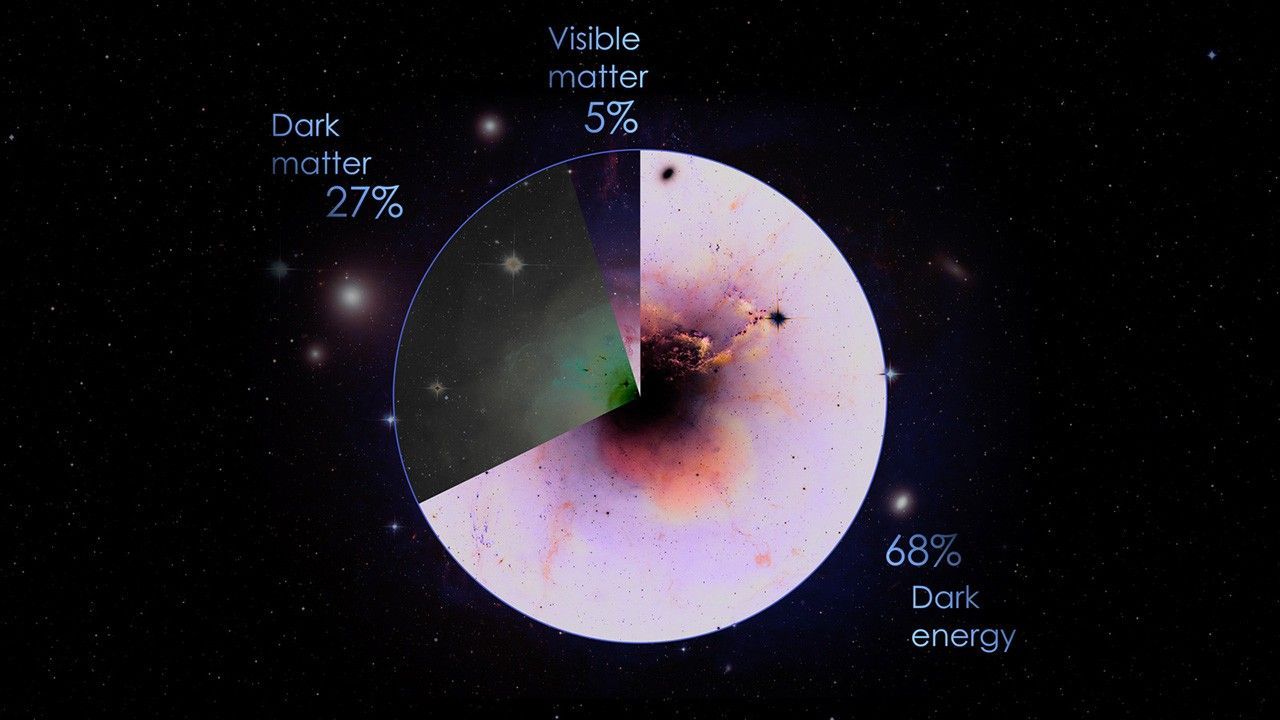
Common or visible case – which forms only 5% of the universe – including anything that we can see in visible light and things can only detect binoculars only on other wavelengths, such as ultraviolet and infrared.

Connected
Largest telescope in the world: a huge leap for space exploration
The world’s largest telescope is as big as your home – and it is unlocking the biggest secrets of the universe.
A material that contains a mass and volume, but cannot be seen directly because they do not reflect, absorb or emit the light, which are dark substances and form about 27% of the universe.
Due to the ghostly qualities of dark matter, even today, scientists are not completely sure what the dark matter is made up of. They said, they Pass It is capable of observing its scaffolding role and impact on visible matters in the universe.
The term “dark matter” was coined by astronomer Fritz Zaviki in the 1930s, and the concept was confirmed by Vera Rubin in the 1970s.
3
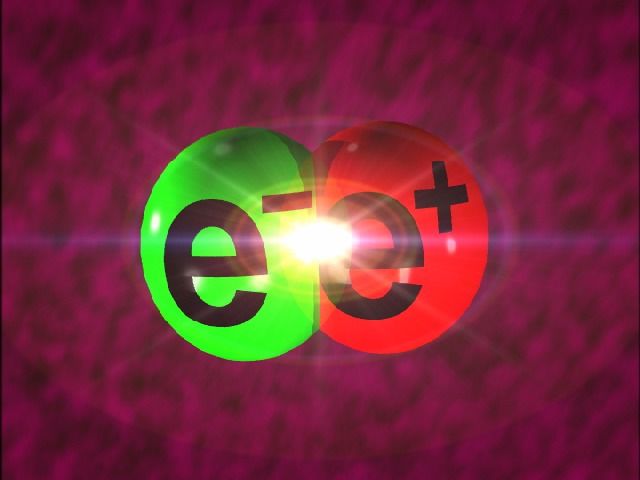
Antiparticles and Antimators
Every type of normal substance in the universe has an antiparticle (perhaps except neutrino). Antiparticles have the same mass to their respective particles, although they have the opposite charge and magnetic field. Antimatter form the result of a combination of antiparticles.
Pairs of particles and antiparticles can be produced in the laboratory through high-energy collisions. The opposite of this process is destruction, which occurs when a particle and its antipartical collides. The vast amount of energy released during this particle-antipartical collision enables scientists to study the basic laws of the universe.
Scientists use Large headron collider In Geneva, Switzerland, to intensify and collide the particles and antiparticles near the speed of light, allows them to study and test the fundamental structure of particle physics and substance.
If Matter and Antimators were built in equal quantity at the time of birth of the universe, none of us would be here today – this case and antimatter would have destroyed each other. However, scientists are still trying to do the work as to why there is such a case in our universe and so low antimatter.
4
Deep energy
While dark matter is invisible structures that keep things together, dark energy is a “force” that is considered to accelerate the expansion of the universe (to a limited extent!). Scientists believe that it creates about 68% of the universe, although it is one of the greatest secrets of the universe.
A popular interpretation of the role of dark energy in the universe depends on that it is an irreversible phenomenon related to cosmological constant. However, other principles suggest that dark energy is a dynamic force shifted over time.

Connected
We also thought of dark energy
The end of the universe can be in question.
5
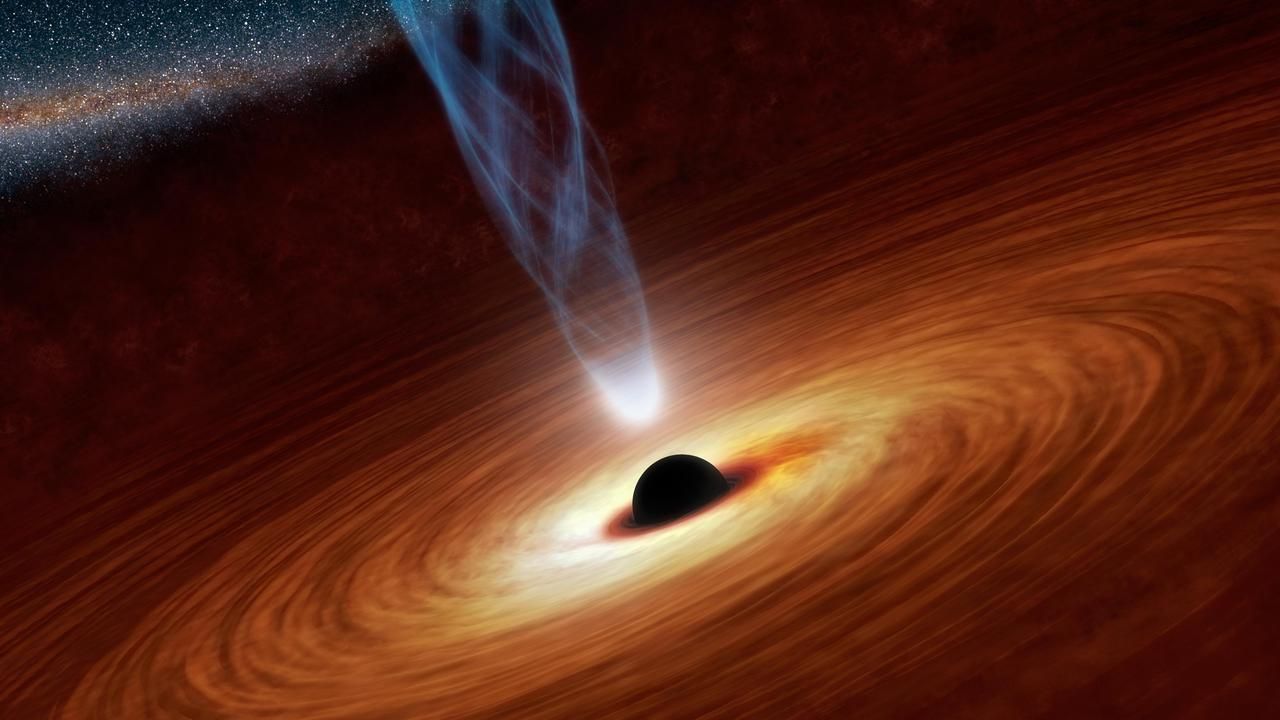
Gully
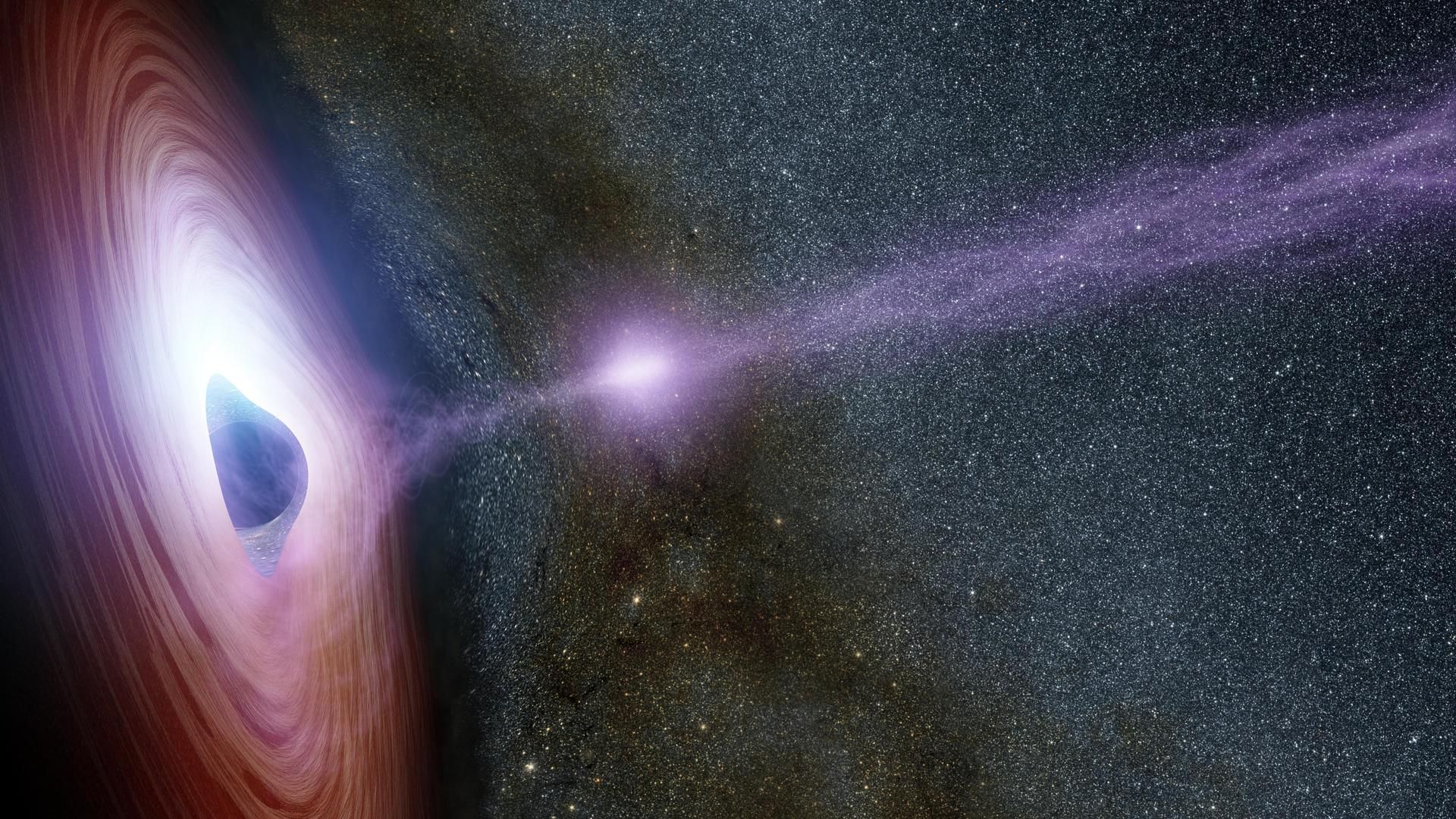
A black hole is a mysterious astronomical object, whose gravity bridge is so important that nothing can survive – even light – not even light – once it passes its event horizon, at which point the velocity required to escape is faster than the speed of light.
Despite not being able to look at the black hole, scientists can observe this powerful event because the matter around it is impacting. The theoretical center of a black hole is known as eccentricity.

Connected
9 misunderstandings you probably have a black hole
Brush on your black hole knowledge.
The three of the three known types of Black Hole are the smallest stellar-dominant black hole, between three to 12 times of the mass of our sun. On the other hand, supermasive black holes, such as Milky Way, can have billions of solar public. There are intermediate-mas black holes (IMBHS), as the name suggests, somewhere between the other two.
Black holes grow when they absorb the surrounding case or other black hole, making them brutally destructive objects. He said, his intense gravitational bridge plays an important role in the Ganges structure, and powerful ejections to be sent beyond the universe can contribute to the formation of new stars from near the pole of Black Hole.
6
Caesar
The most bright objects in the universe are the core of the galaxies in the universe, the core of the galaxies in the universe, fuel by supermasive Black Hole.
As the case is drawn towards a black hole, it collects in a cloud spiral called the granular disc. The inner parts of this disc travel much faster than the exterior, which causes so much friction and heat that it shines to trillions of our sun’s time.
The combination of heat in the granship disc and rejection of powerful jets of the substance near the poles of black holes makes the most bright quaser to see the most bright quasar through binoculars on the earth.

Connected
How to choose the best binoculars for a start
From one beginning to another.
7
Cosmic rays
Cosmic rays are highly energetic particles or particle groups from outer space that travel slightly under the speed of light (just less than 300 million meters per second). They are manufactured by our Sun, other stars and far-off events such as Black Hole and Supernova blasts.
Solar cosmic rays usually have lower energy than the Milky Galactic cosmic rays (most abundant in our surrounding area), while extragactic cosmic rays are generally considered the most powerful. The Earth’s magnetic field protects us from most possible damage caused by cosmic rays, deflections of most of the particles charged away from our planet, before the atmosphere is absorbed and spreads what is left.

Connected
7 Surprising facts you would never have heard about Earth’s core
The center of our planet is much more complex than your expectation.
8
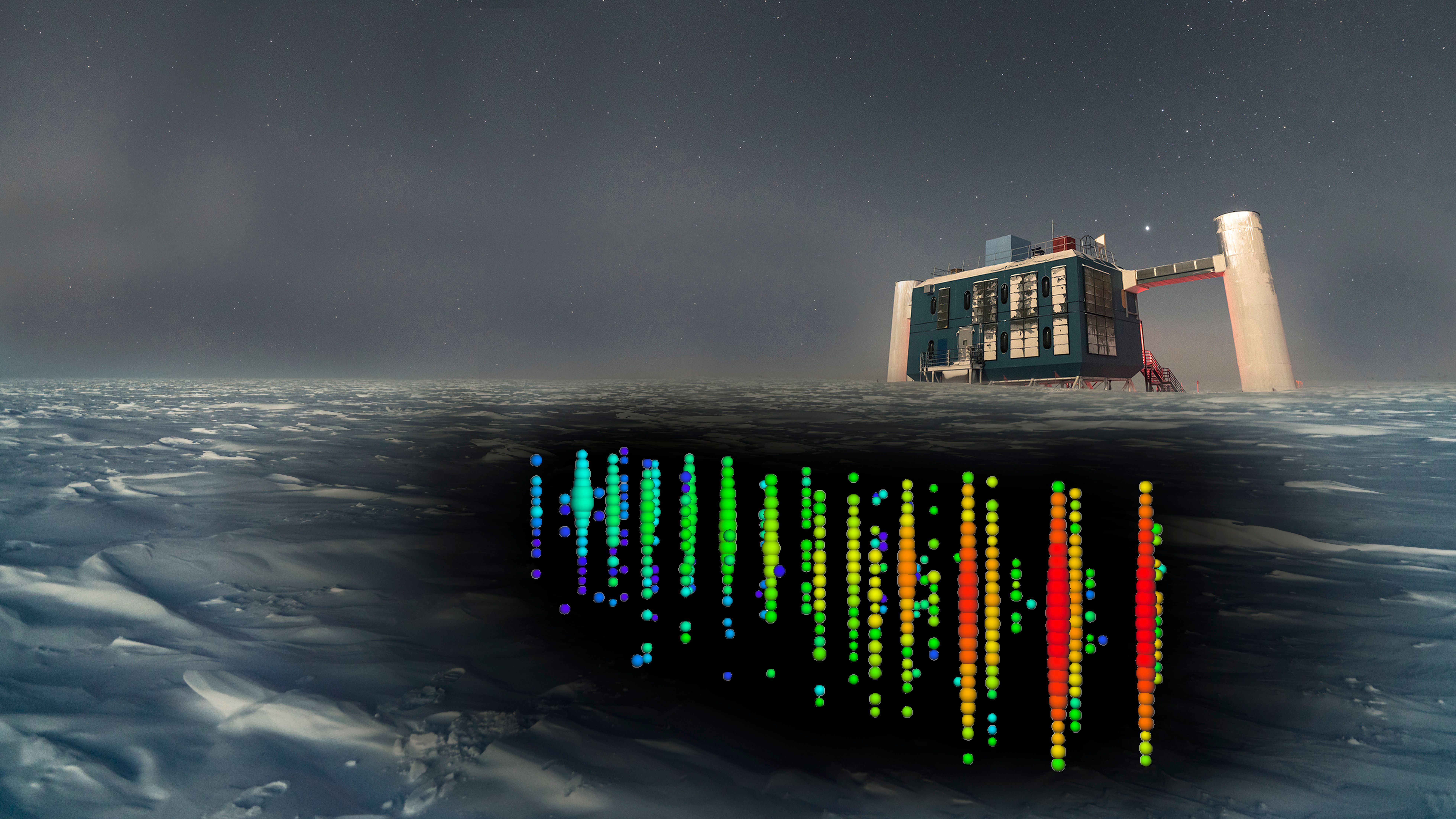
Neutrino
Neutrinos are small and almost large-scale sub-atomic particles, produced in cosmic events such as supernova explosion, gamma-rash, stellar fusion and nuclear decay. They take information about the incidents that they traveled to millions or even billions of lighting through cosmos.
However, because their interactions with other cases are minimal, they are particularly difficult to inspect. Actually, billions of neutrinos from the Sun pass through us and our planet, which pass through us without going to us.
He said, scientists have developed special detectors – such as Icube neutrino observatory In Antarctica-who observe rare opportunities when neutrino collides with the substance, leading to the understanding of the universe, expansion, and dark-known events, such as the origin, expansion and dark matter.
9
Light year
A light-year is a distance light journey in an Earth year.
Because the distance in space is so large, standard units of measurement – such as miles or kilometers – can be very difficult for fathom. A light-year is 9.46 trillion kilometers or 5.88 trillion miles, and the distance between Milky Way Galaxy and our neighbor, Andromeda Galaxy is about 205 million light-year.

Connected
5 Wonderful Nakshatra and why you should know them
There is a lot to look up!
Along with measuring the distance between celestial bodies, light-year is used to determine the size of large objects in the universe. For example, the Milky Way Galaxy is about 105,700 light-year crossing.
10
Astronomical unit
Previously, a celestial unit (AU) was the average distance between the center of the Earth and the center of the Sun. However, in 2012, the International Astronomical Association standardized AU as 149,597,870,700 meters, or just 92,955,807 miles, to correspond to the international system.
Any man-made object has not traveled beyond the Earth compared to the Vyzer 1 probe, which is about 166AU away from our planet until May 2025.
Scientists mostly use AU measurements to specify the distance in a familiar, relative solar system.