When you put your hand out of the window of a moving car, you think that Force pushed against youThis force opposes a moving vehicle, and it is part of the reason that your car naturally slows down at a stop if you remove your foot from the gas pedal. But the drag does not just slow down cars.
Aerospace engineers are working on using drag force in space to develop more fuel-skilled spacecraft and mission, deorbit spacecraft to develop more fuel-skilled spacecrafts Space junkAnd even space Investigation in orbit around other planets,
Space is not a complete vacuum – at least not all. Earth’s atmosphere Gets diluted with heightBut it has enough air to revolve on the spacecraft. 620 miles (1,000 km).
In form of Aerospace engineering professorI study how the drag affects the movement of the spacecraft in the orbit. DescendantAs the name suggests, there is a type of maneuver that uses thin air in space, which applies a drag force in the opposite direction of the speed of a spacecraft, like braking in a car.
Change a class
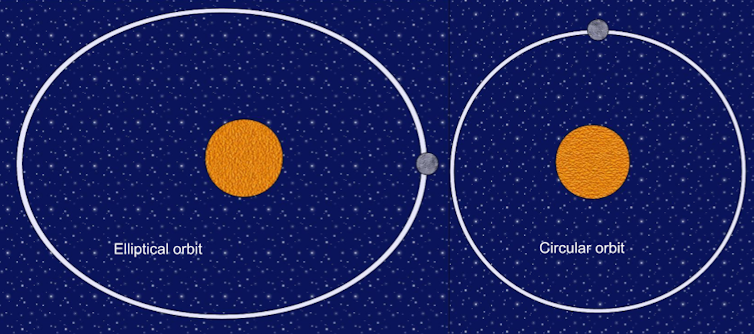
In space, aerobreaking can change the orbit of a spacecraft by reducing the use of its propulsion system and fuel. The spacecraft does classes around the Earth Two types of classes: Circular and elliptical. One in Spherical classThe spacecraft is always at the same distance from the center of the Earth. As a result, it is always moving at the same speed. An elliptical orbit is stretched, so there is a distance and speed move from the earth, which travels with the orbit of the spacecraft.
The nearest point in an elliptical orbit around the Earth, where the satellite or spacecraft is moving the fastest forward, PerigeThe farthest point, where it is running slow, is called Unseen,
The general idea behind aerobreaking is to start in a large circular orbit and the spacecraft maneuver in a highly elliptical orbit, so that the lowest point in the orbit, perigri, lies in the dense part of the upper environment. For the Earth, it is between 62 and 310 miles (100 and 500 kilometers), which is with the choice on the time required to meet class changes.
As the spacecraft passes through this lowest point, the air puts a drag force on it, which reduces the stretch of the orbit over time. This force draws craft to a circular orbit compared to the original class.
Money/Wikimedia Commons, CC by-SA
The first maneuver to put the spacecraft into an elliptical orbit is required to use a propulsion system and some fuel. But once it is in the elliptical orbit, pull from the atmosphere slow the craft, and there is no need to use it too much, if any, the fuel.
Aerobracing brings a craft from a large class to a small class and is not reversible. This cannot increase the size of a class. Pranation and fuel are required to increase the size of a classroom or increase spacecraft into a higher orbit.
Uses aerobracing
A common case where the Spacecraft Controller uses aerobracing when changing the orbit of the craft A geostation class– Earth. Low Earth orbitLeo. A land class is a circular class with a height of about 22,236 miles (35,786 km). In Jio, the spacecraft forms an orbit around the Earth in 24 hours, so the spacecraft is always above the same point on the surface of the Earth.
Prior to aerobracing, the onboard propulsion system of the spacecraft emphasizes in the opposite direction of the speed of the Jio orbit. This emphasis puts it in an elliptical orbit. The craft several times passes through the atmosphere, which eventually circulates the orbit.
Once it makes Leo, the spacecraft may need to use a little fuel to motivate itself in its goal class. Typically, the lowest point of the original elliptical class is less than the final goal circular class.
How is this process ideologically identical US Space Force’s X -37B used aerobreaking in early 2025US Space Force told that its Unmanned Spaceplane, X -37BUsed aerobracing. This test demonstrated the agility and dynamics of the craft.
Another application for aerobracing is to create a spacecraft deorbit deauthing or rebuild the atmosphere after stopping working. In this way, the company or agency can settle and survive the spacecraft. Space junkSince it will burn in the lower environment.
Aerobreaking for mutual mission
Some Mars missions, including Mangal reconnaissance orbiter And this Mangal Odyssey OrbiterAerobreaking is used to reach its goal classes around the red planet.
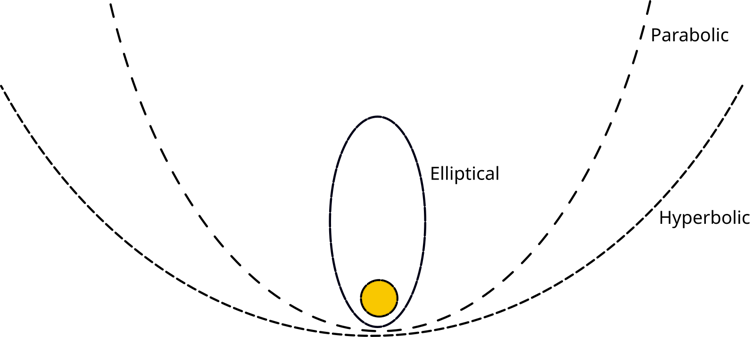
For interplanetary missions such as these, scientific crafts use aerobracing in combination with the onboard propulsion system. When a spacecraft comes to Mars, it happens in one Exaggeration,
Maxmath12/Wikimedia Commons
Unlike a circular or an elliptical orbit, the path of spacecraft in hyperbolic orbit will not revolve around Mars. Instead, it will fly through Mars and does not use the emphasis from its propulsion system to get “capture” in a closed elliptical orbit.
As the spacecraft falls on Mars, the propulsion system on the ship set fire to providing the spacecraft to catch the Mars in a highly elliptical orbit. Once captured, scientists use aerobrecking on several orbital passes through the atmosphere to achieve the final orbit, usually a spherical.
Aerobreaking maneuvers can result in significant fuel savings. Like humans come closer Red planetary surfaceAerobreaking can save fuel saving mass and allow each spacecraft to be taken to Mars to allow more supply.
In the grand arch of space exploration, aerobreaking is not just a maneuver. It has an important role in the future of space operations and planetary missions and colonies.
Piyush MehtaAssociate Professor of Space systems, West Virginia UniversityThis article has been reinstated Conversation Under a Creative Commons License. read the Original article,
![]()


