Ten vendors may be exploited to steal weaknesses affecting a Bluetooth chipset in more than two dozen audio equipment or to steal sensitive information.
Researchers confirmed that 29 devices are affected by berradionamic, Bose, Sony, Marshall, Jabra, JBL, JLAB, Eyrismx, Moerlebes and Tefel.
The list of affected products includes speakers, earbuds, headphones and wireless microphones.
Security problems for taking a weak product can be availed and on some phones, an attacker within the connection range may be able to remove call history and contacts.
Snuping on a Bluetooth connection
But Soldier Security Conference in Germany, researchers at Cybercity Company revealed three weaknesses in aeroha systems on a chip (SOCS), which are widely used in True Wireless Stereo (Tids) Yearbuds.
Issues are not important and in addition to close physical proximity (Bluetooth range), their exploitation also requires “a high technical skill set”. He received the following identification:
- CVE-2025-20700 (6.7, Medium Severity Score)-missing certification for GATT services
- CVE-2025-20701 (6.7, Medium Severity Score)-Missing for BR/EDR
- Cve-2025-20702 (7.5, high severity score)-Important capabilities of a custom protocol
Researchers at ERNW say they created a proof-of-concept explopit code, which allowed them to read the media currently playing with the target headphones.
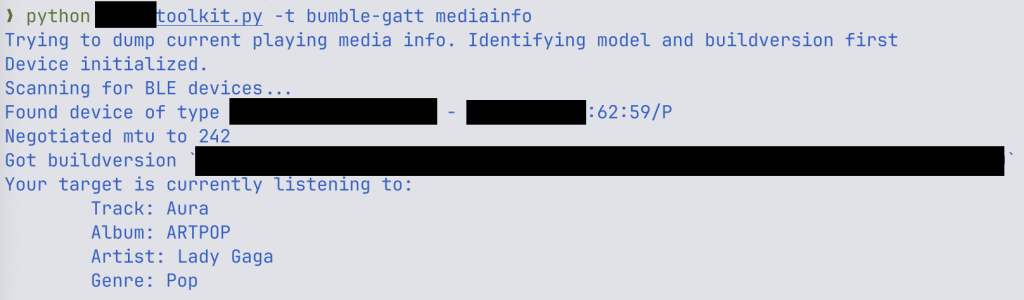
Source: Erwn
Although such an attack may not have a major risk, the other landscape can hijack the connection between a mobile phone and an audio Bluetooth device to a danger actor taking advantage of the three bugs and uses Bluetooth hands-free profile (HFP) to release commands on the phone.
“The limit of the available command depends on the mobile operating system, but all major platforms support the least start and receiving the call” – – ERNW
Researchers were able to trigger calls to an arbitrary number by removing the Bluetooth link from the memory of a weak device.
They say that based on the configuration of the phone, an attacker can also recover call history and contacts.
They were also capable of starting a call and “successfully evsdrop on conversations or sounds within the earshot of the phone.”
In addition, the firmware of the weak device can possibly be re -written to enable remote code execution, which may facilitate the deployment of an artificial abuse capable of promoting in many devices.
Attack restrictions apply
Although ERNW researchers present serious attack scenario, the practical implementation on the scale is forced by certain limitations.
“Yes – the idea that one can kidnap your headphone, impress them towards your phone, and potentially you can call or spy on you, seem very dangerous.”
“Yes – technically, it’s serious,” researchers say “are complex to perform real attacks.”
The requirement of both technical sophistication and physical proximity limits these attacks to high-value goals, such as diplomacy, journalism, activism or sensitive industries.
AIROHA has released an updated SDK that includes the required mitigations, and device manufacturers have started patch development and distribution.
Still, German publication Part says The most recent firmware updates for more than half of the affected equipment are 27 May or before, which is distributed to its customers before Aeroha.



