The data verification tool of Microsoft Excel lets you add a drop-down list to the cell based on the existing data in a column. However, how it works depends on whether the source data is part of a formitted Excel table. Let’s take a look at some examples.
Using a column in a formatched Excel table
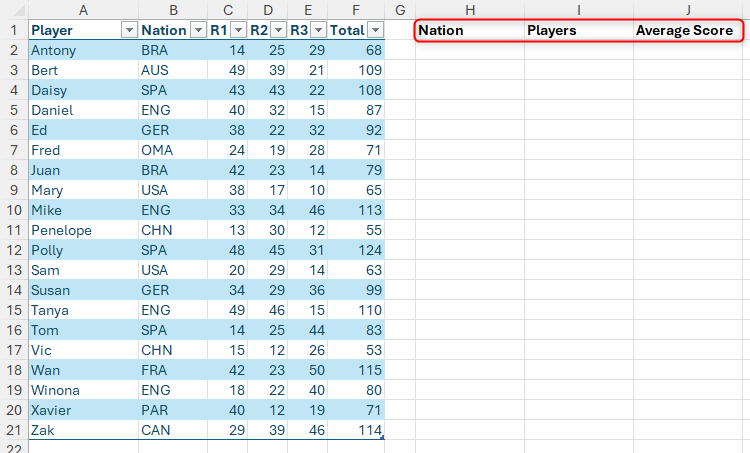
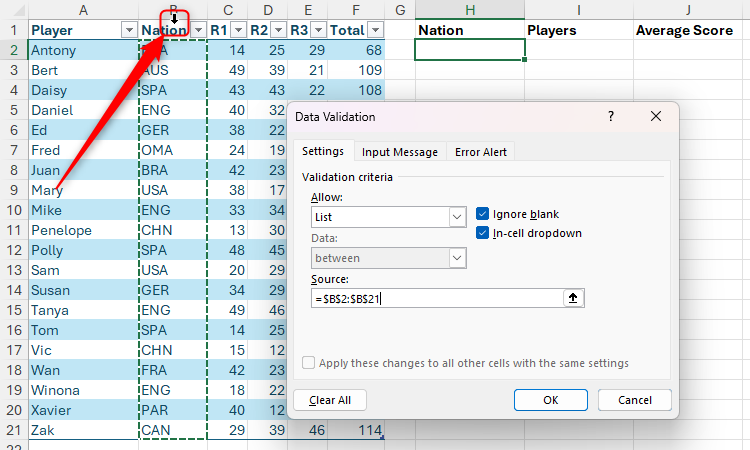
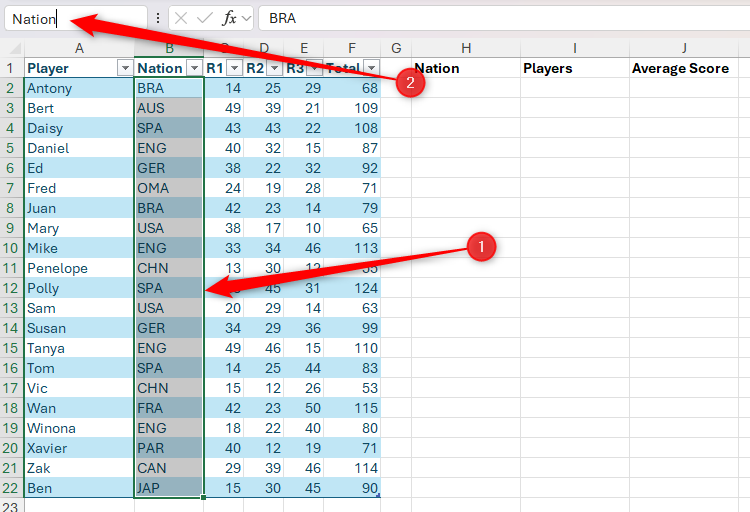
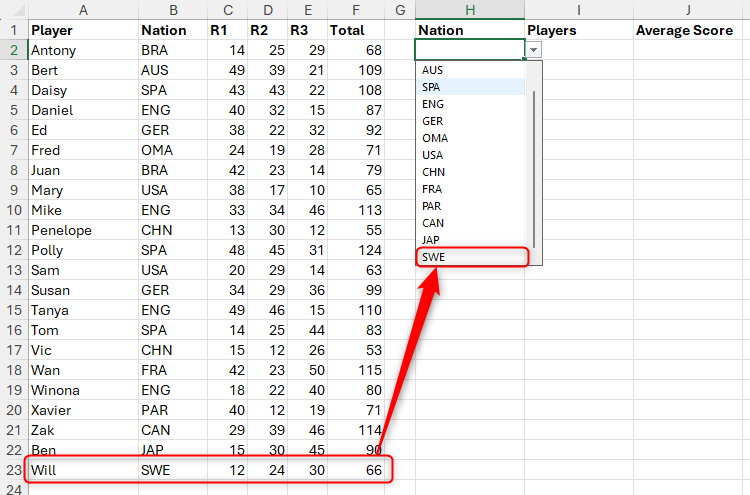
Imagine that you have this formatted Excel table, named “Score” that has a player’s name, nation and score, and you need to extract some summary data. In particular, in SAIL H2, you want to make a drop-down list of all nations listed in column B, and in cells i2 and J2, according to the selected nation, display the player’s name and average score respectively.
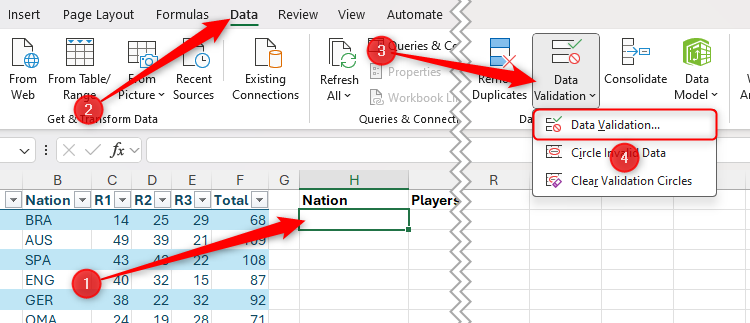
To make a drop-down list, select the cell where you want it (in this case, cell i2), and in the data tab on the ribbon, click “Data Verification” in the drop-down option with the same name.
Connected
How to add drop-down list to a cell in Excel
It separates typing in the same option manually 200 different times.
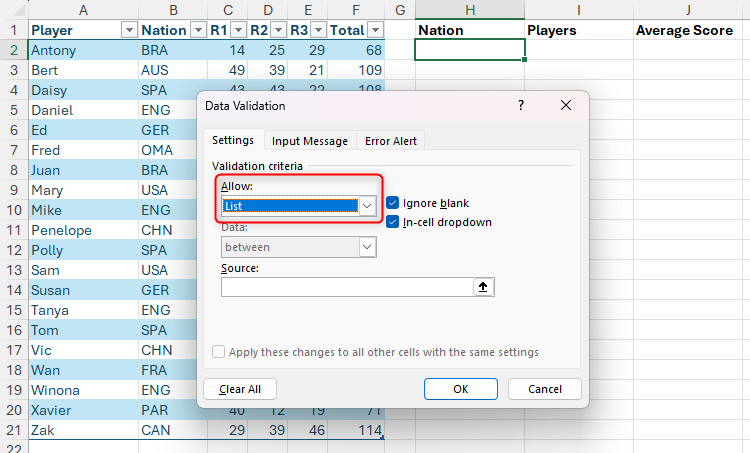
Then, in the permission of the area of the settings tab, choose “list”.
The next stage involves inputting options that you want to display in the source field on the drop-down list. To do this, you can type the option manually, select the related cells on your spreadsheet, or use a formula.
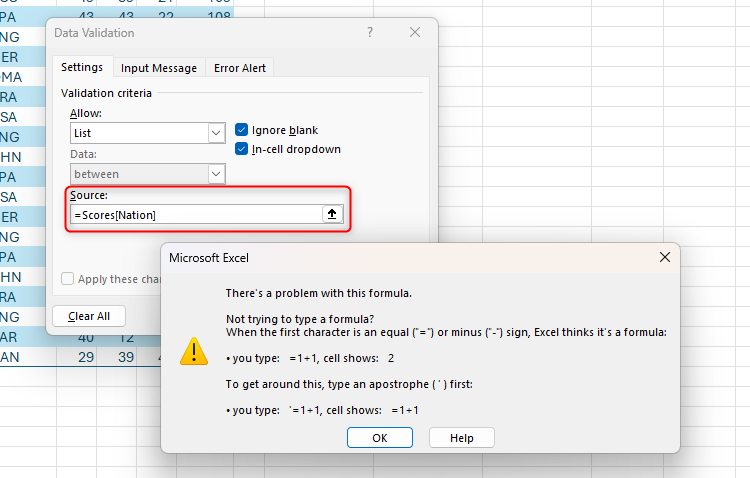
Ideally, you will be able to type:
=Scores(Nation)
In the source area, in the same way as you refer to the column in a formula, where the “score” represents the table name, and the “nation” represents the column header. However, unfortunately, it gives an error message, because data verification tool only recognizes cell references, formulas, and as data sources to the designated range, not the table column header.
Fortunately, there are two ways to go around it.
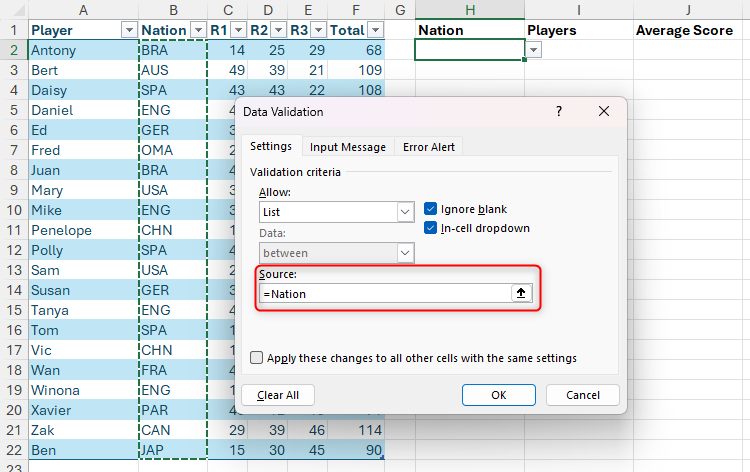
Method 1: Referred to cells in the table
First, activate the “source” field in the data verification dialog box so that the cursor is shining, and the relevant column in row 1 hover on the header until you see a small, black down arrow. When you do, click once to select all data cells in that column.
Be careful not to select the entire column by clicking on the appearing arrow when you hover the column reference letter (in this case, in this case, as it is, as it will choose the entire column, including the header in Row 1 and the cells below your table. You have successfully selected the correct limit if cells are surrounded by a dotted line only in the column within the table.
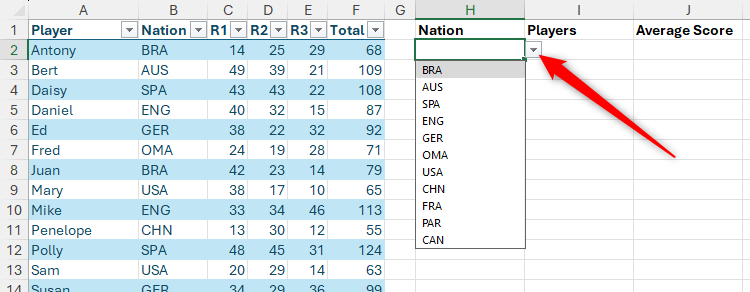
Now, after clicking on “OK”, when you select the Cell H2, a drop-down button appears, which you can click to select an option from the source. Note, also, how unique values are displayed in the list – in other words, Excel recognizes duplicate values, and only displays them once.
Data verification in Excel adopts the same order as a drop-down list source. In this example, to order nations in the alphabet, you have to sort the source data by column B.
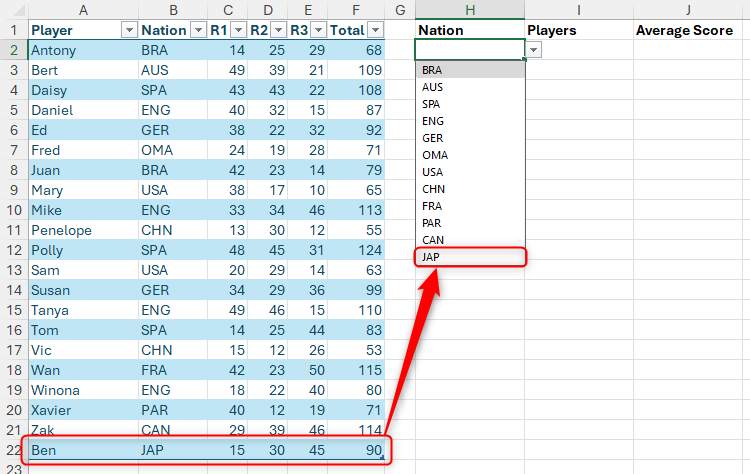
The beauty of using this method is that if you add more rows to the format Excel table, the data verification sources automatically adjust to the additional cells or cells.
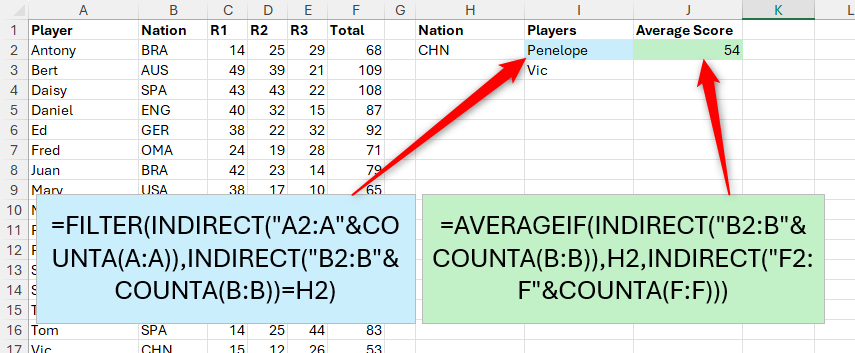
Now, you can use the filter function in Sale I2 to list the players of the selected nation:
=FILTER(Scores(Player),Scores(Nation)=H2)

Connected
How to use filter function in Microsoft Excel
There are more than one way to filter your data.
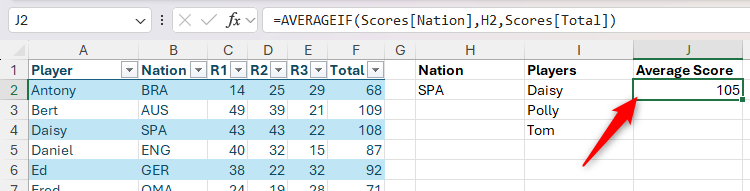
Finally, use the average function in SAIL J2 to display the average score of players of this nation:
=AVERAGEIF(Scores(Nation),H2,Scores(Total))

Connected
How to use average and average tasks in Excel
Be selective about what to include in your average calculation.
Method 2: Range Name
The format table includes the second way of making a drop-down list from a column.
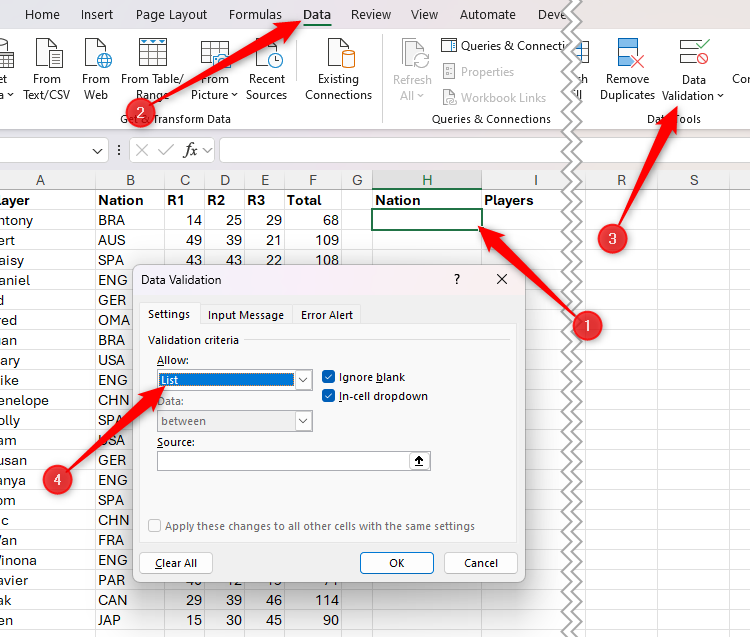
Before launching the data verification dialog box, select all cells in the table that include the values you want to include in the drop-down list, type a name for the range in the name box in the top-left corner of Excel Window, and press the Enter.
To keep things simple (and memorable!), The name recorded for you selected should be similar to the column header.
Then, in the source field of the data verification dialog box, type a uniform sign (=), then by the name you had assigned to the range, and press Enter. In this example, you need to type:
=Nation
With the previous method, Excel assumes that the data is in a formatted table, so it automatically expands the boundary if the data is added to the next line.
Excel has many benefits of using the designated range. For example, the nomenclature range makes your workbook more accessible to people using screen readers. In addition, you can select them from options quickly by typing in the name box or clicking down arrows, and can also select the designated range in names, and names can also be used in formulas.
Connected
I always name the range in Excel, and you also need
Clean your Excel workbook.
Now, with method 1, you can use filters and auspicious tasks to meet data extraction.
However, this time, the formula can be more straightforward, as you can refer to the range you named “Rashtra”, the table in which the table is referred to.
So, for filter in SAIL I2, it is:
=FILTER(Scores(Player),Nation=H2)
And for average in cell J2, it is:
=AVERAGEIF(Nation,H2,Scores(Total))
Using a column in an unpublished dataset
Some types of data-like splied ares-axel can be formed as a table, so there may be times when you need to find a way to create a drop-down list from a column within an unforgettable dataset.
After selecting the cell, in which the drop-down list will be held and clicking “data verification” in the data tab on the ribbon, select the “list” in the permission field.
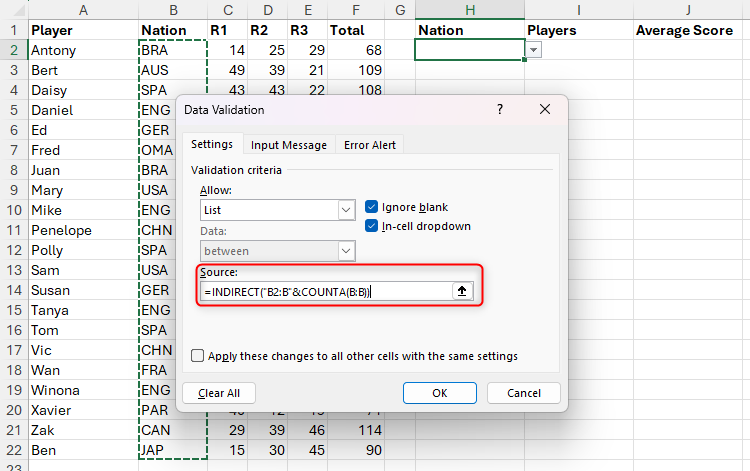
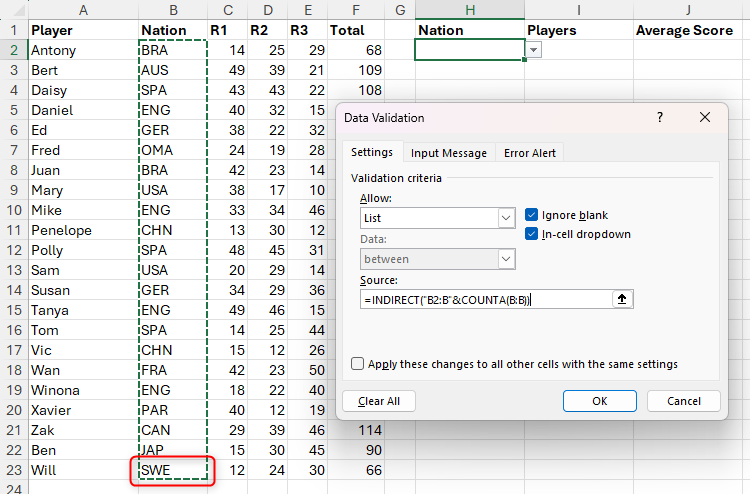
Next, in the source field, use the indirect and counta functions to explain where to find the drop-down list options.
In this case, typing:
=INDIRECT("B2:B"&COUNTA(B:B))
The column B from Cell B2 to Cell B22 as source includes all values.
Let us break the formula of this source about how it works.
- = Indirect (:: This tells Excel that you want the source to be determined using a dynamic context.
- “B2: B”: In particular, the dynamic reference begins on cell B2, and ends on another cell in column B.
- & Counta (b: b): It counts all cells in column B that are not empty, and add total in context. In this case, column B has values in 22 cells, so it converts B2: B into B2: B22.

Connected
How to use indirect function in Excel
Use a text string to make a reference.
Therefore, if you add another line of data below, the counta function will pick it up and indirectly indirect reference to the data verification rule that the source has expanded downwards by an additional row.
Using a formula to determine which values to include in the data verification source-the conquest is considered the best practice rather than selecting the entire column because it prevents the header row and empty rows from joining the drop-down list.
You can check it again by selecting a cell hosting the drop-down list and reopening the data verification dialog box. When you choose the source field, even if the formula has not changed, the dotted line on the spreadsheet confirms that the couple lifts new values in the row.
Now that your drop-down list is ready to go, use indirect and counta functions with filter functions in SAIL I2 to complete the spreadsheet and an average function in cell J2.
The drop-down list added through data verification tools is incredibly powerful and versatile, and can be used in many scenarios in Excel. For example, you can use drop-down lists to make regular charts dynamic-a certain way to impress your friends and colleagues.