
Hackers have adopted a new technology called ‘Filefix’ in the interlock ransomware attacks to release a remote access trojan (RAT) on targeted systems.
The interlock ransomware operations have increased in the previous months as the danger actor has started using Kongtuk web injector (aka ‘Land update 808’) to distribute payload through compromise websites.
This change in Modus operandi was seen from May from May by researchers on DFIR reports and proofpoints. Subsequently, visitors of the compromised sites were motivated to pass a fake captcha + verification, and then pasted into a run dialogue material, which was automatically saved on the clipboard, a strategy to suit the clickfix attacks.
Tricks inspired users to execute a powerrashel script, bringing and launching a node.JS-based version of the interlock rat.
In June, the researchers found a PHP-based version of the interlock rat used in the wild, which was given using the same Kongtook injector.
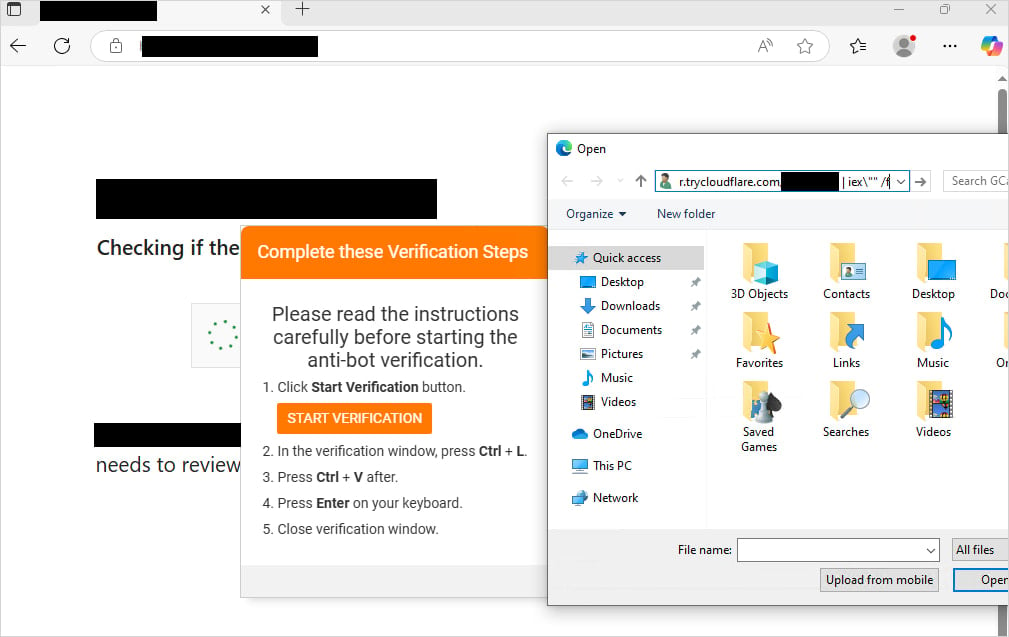
Earlier this month, a significant change in the delivery cover occurred, in which the interlock is now switching to the filefix variation of the clickfix method.
Source: DFIR Report
Filefix is a social engineering attack technique developed by security researcher MR.D0X. It is a development of the clickfix attack, which became one of the most widely planned payload distribution methods compared to the previous year.
In FileFix variation, the attacker gives weapons to reliable Windows UI elements such as file explorers and HTML applications (.HTA) to trick users to execute malicious powerrashels or JavaScript code without displaying any security warning.
Users are motivated to “open a file” by pasting copied string into the address bar of the file explorer. The string is a powershell command that is disturbed to look like a file path using comment syntax.
In recent interlock attacks, the goals are asked to paste the command -up with a fake file path on the file explorer, leading to downloading Php rats from ‘Trycloudflare.com’ and leading to its execution on the system.
After the infection, the rat executes a series of power sugar commands to gather systems and network information and exfiltrate this data as a structured JSON for the attacker.
Dfir report Active directory calculation, checking for backup, navigating local directions and evidence of interactive activity including domain controllers are also mentioned.
Command and Control (C2) can send shell commands to execute the shell command for the server rat, introduce the new payload, add firmness through the registration run key or to move later via remote desktop (RDP).
The interlock ransomware was launched in September 2024, claiming notable victims such as Texas Tech University, Davita and Catering Health.
The ransomware operation leveraged the clickfix to infect the goals, but its pivoting for the FileFIX indicates that the attacker is quick to suit the methods of the silent attack.
This is the first public confirmation of the filefix being used in the actual cyber attack. This is likely to gain more popularity as the danger actors detect ways to include it in their attacks.



