
The Lumma Infostealer Malware Operation is slowly resumed after a large -scale law enforcement operation in May, resulting in seizure of 2,300 domains and parts of its infrastructure.
Although the Lumma Malware-AA-A-Service (MAAS) platform faced significant disruption from law enforcement action, as the report on the infostealer activity was confirmed in early June, it did not stop.
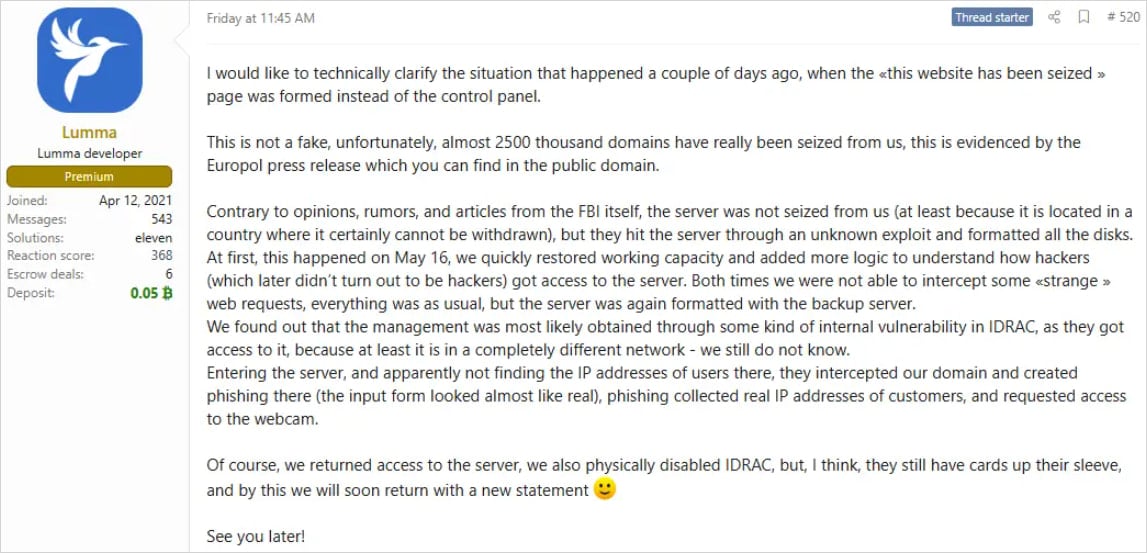
Operators immediately accepted the situation on the XSS forums, but claimed that their central server was not seized (although it was erased from a distance), and the restoration attempts were already running.
Source: Trend Micro
Gradually, MAAS rebuilt and gained confidence within the cyber crime community, and is now facilitating operating operations on many platforms again.
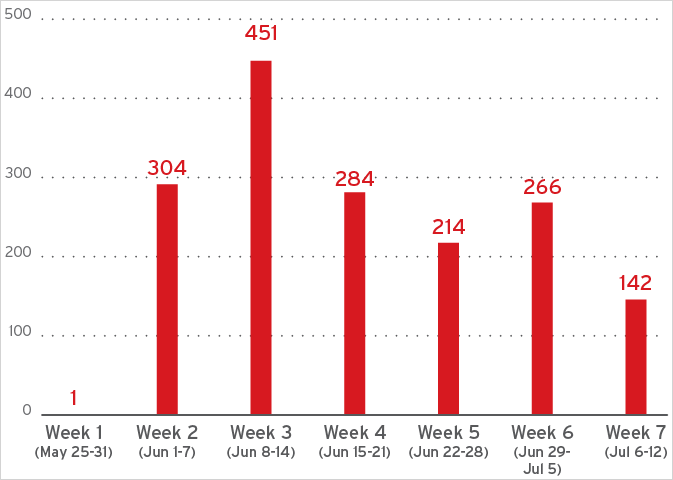
According to trend micro analysts, Lumma has returned to almost pre-pre-activity levels, indicating rapid reconstruction of infrastructure with a cyber security firm’s telemetry.
“After law enforcement action against Lumma Staller and its affiliated infrastructure, our team has seen obvious signs of revival in the operation of Lumma,” Trend reads micro report,
“Network telemetry indicates that Lumma’s infrastructure began to re -ramps within the week of Techdown.”
Source: Trend Micro
Trend Micro reports that Lumma still uses a valid cloud infrastructure to mask malicious traffic, but is now transferred from cloudflair to alternative providers, mostly to the Russian-based cellle, which is meant to avoid the takedown.
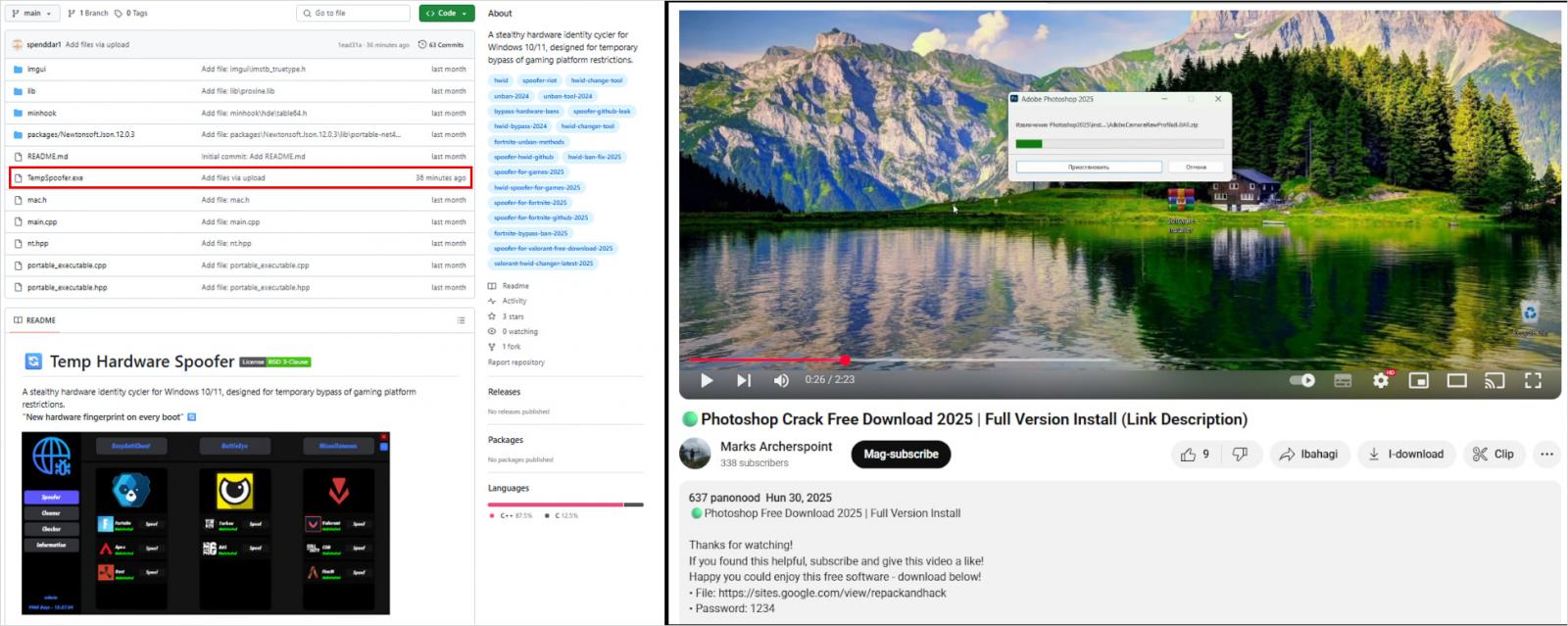
Researchers have highlighted four distribution channels that Lumma currently uses to achieve new infections, indicating full-dominated for versatile targeting.
- Fake cracks/keigns: Fake software cracks and keygins are promoted through malwartizing and manipulated search results. The victims are directed to misleading websites that finger their system using the traffic detection system (TDS) before serving Lumma Downloader.
- Clickfix: The compromised websites display fake captcha pages that trick users to run the powershel command. These commands load Lumma directly into memory, which helps to avoid file-based detection mechanisms.
- Github: Attackers are actively making github repository with AI-bounded content advertising advertising advertisement fake game cheating ingredients. These repo host lumma payload, such as “tempspoofor.exe”, either in executable or zip files.
- YouTube/Facebook: Current lumma distribution also includes YouTube videos and Facebook posts that promote cracked software. These links host lumma malware to external sites, which sometimes misuse reliable services like reliable services.
Source: Trend Micro
The re -emergence of Lumma as an important threat suggests that law enforcement action, devoid of arrest, or at least prosecution, is ineffective in stopping these prescribed danger actors.
MAAS operations, such as Lumma, are incredibly profitable, and the leading operators behind them see law enforcement action as regular obstacles, they only have to navigate.



