
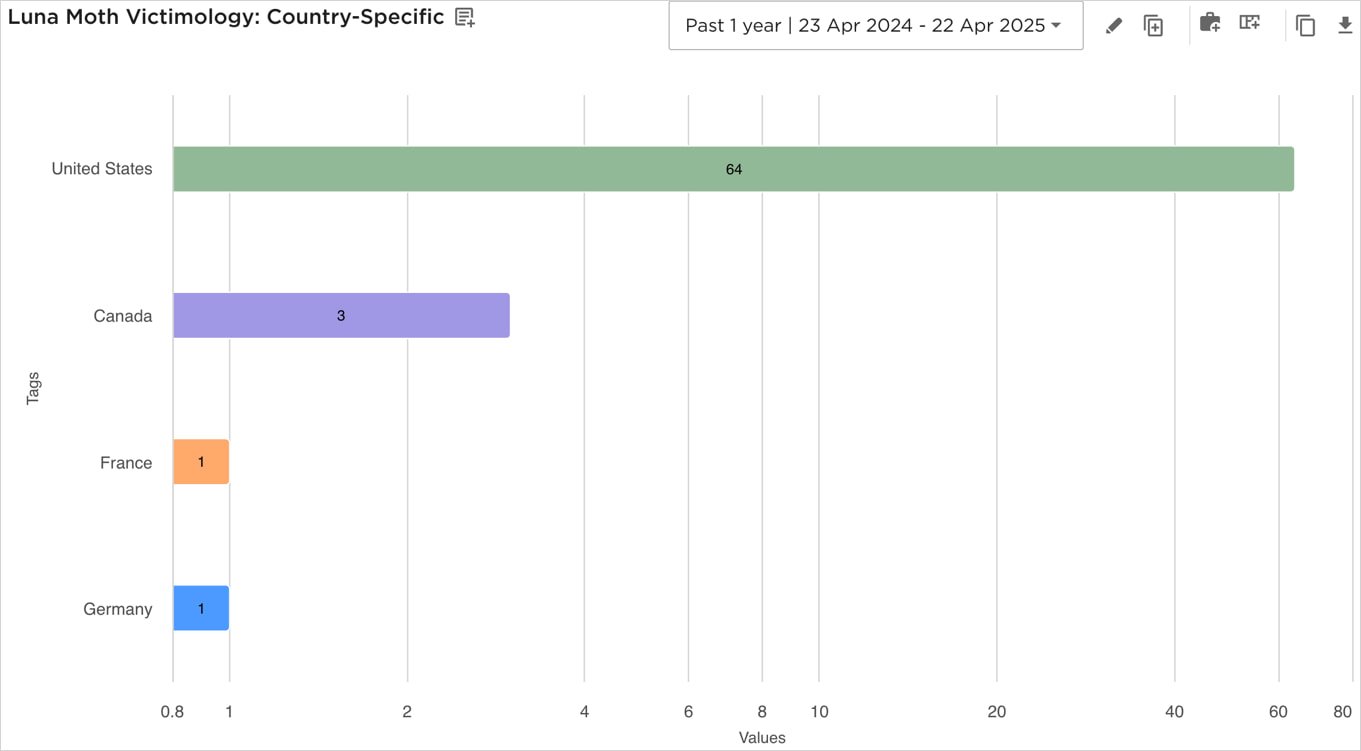
Luna Moth, aka Silent Ranesam Group, has increased the callback phishing operations in attacks on legal and financial institutions in the United States, known as the Silent Rances Group.
According to EclecticIQ researcher Arda Büyükkaya, the ultimate goal of these attacks is data theft and forced recovery.
Luna Moth, who is internally known as the Silent Ranesam Group, is a danger actor, who first launched the Bazarkal campaign as a way to achieve the initial access to the corporate network for Ryuk, and later, for the Constable Rancemware attacks.
In March 2022, as Conti began to shut down, the Bazarkal actor separated from the danger Contic Syndicate and created a new operation called the Silent Rainsm Group (SRG).
The latest attacks of Luna Moths include incorporating IT support via email, fake sites and phone calls, and completely rely on social engineering and deception, in which no ransomware is seen in any case.
“By March 2025, EclecticIQ assesses with high confidence that Luna Moth has recorded at least 37 domains through Godaddy to support its callback-firing operations,” EclecticIQ reads reports,
“Most of these domains apply it to helpdesk or support portals for helping helps or financial services firms, which use typosyted patterns.”
Source: Eclecticiq
The latest activity observed by EclecticIQ begins in March 2025, targeting US-based outfits with malicious emails, which include fake helpdesk numbers, is urged to call to solve non-existent problems.
A luna moth operator responds to the call, replicates the IT employees, and fakely assures to install the remote monitoring and management (RMM) software, which helps the desk sites that give the attackers remote access to their machine.
Fake aid desk sites use domain names that follow the naming pattern (Company_name) -Helpdesk.com and (Company_name) Helpdesk.com.
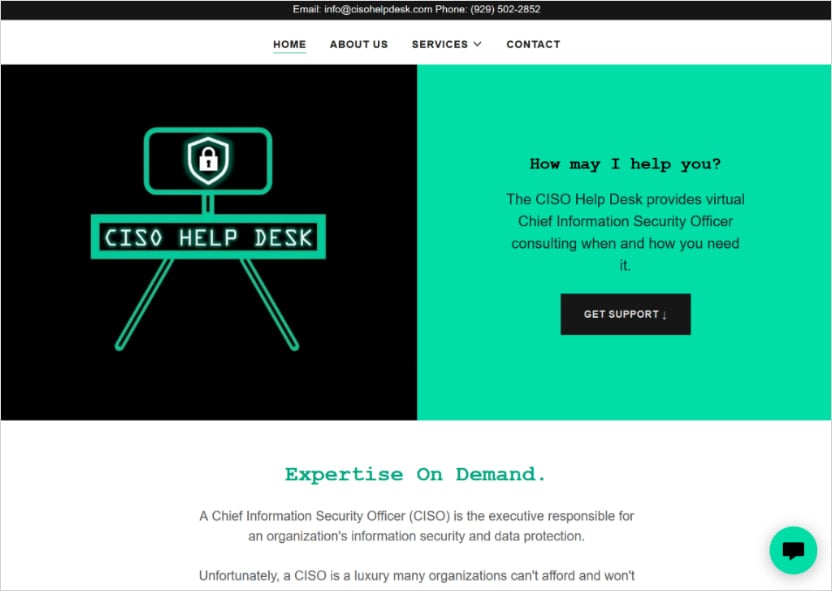
Source: Eclecticiq
Some of the equipment misbehaved in these attacks are Sinkro, Supels, Zoho Assist, Etera, Anidek and Splashtop. These are valid, digitally signed tools, so they are unlikely to trigger any warning for the victim.
Once the RMM tool is installed, the attacker has the keyboard access, allowing them to spread in other devices and find local files and search for shared drives for sensitive data.
After being located in valuable files, they exercise them for an attacker-controlled infrastructure using WINSCP (via SFTPP) or RCLONE (Cloud Sinking).
After the data stolen, Luna contacts the moth -affected organization and threatens to publicly leaked it on its clearweb domain until they pay ransom. The amount of ransom is perfect, which ranges from one to eight million USD.
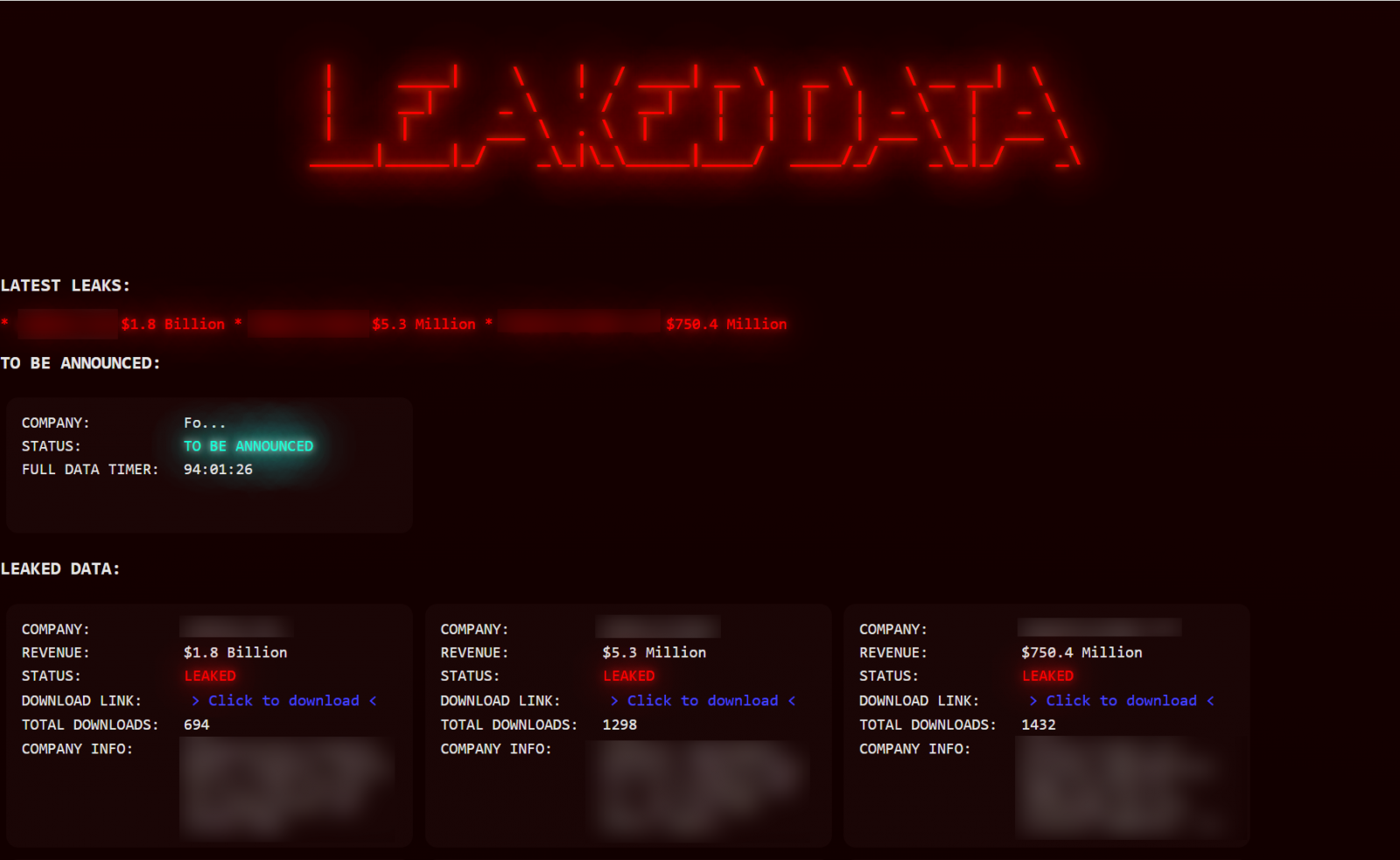
Source: Bleepingcomputer
Büyükkaya comments on the secret of these attacks, given that they do not include any malware, malicious attachment, or links to malware-grid sites. The victims install only an RMM tool, thinking that they are receiving help desk support.
As the enterprise usually uses these RMM tools, they are not marked by safety software as malicious and allowed to run.
Indicators of compromise (IOCs) including IP addresses and fishing domains, which should be added to a block, are available at the bottom of the Eclecticiq report.
In addition to the domain, it is also recommended to consider restricting the execution of RMM tools that are not used in an organization’s environment.



