There used to be all anger among overclocking gamers and other PC enthusiasts, but new techniques have made it irrelevant to most situations. And the best part? To get the same allowances, you do not have to do anything.
What is overclocking?
Everything on your PC runs on a certain frequency (speed of your clock), which is why you usually see the CPU speed expressed in terms of gigahrts. A CPU that is driving 3 gigahrts will ride a bicycle three billion times per second, and is capable of operating in a certain number in every cycle. As a result, if you want your PC to do more things (operate) rapidly, then you need to increase your watch rate.

Connected
What is the meaning of clock speed and why is it not the only factor to choose CPU
Tick, talk, is this a clock?
For years, this desire to squeeze better and better performance than CPU (and other PC components) has led PC enthusiasts to overclock their PCs – to run the clock speed above its designed range.
Overclocking is not the same as a dial to bend, though. The frequency of a high clock usually requires more power, which works hard to every component between the power supply and the CPU. Eventually, it is going to give something in that series of components. A capacitor can blow up, a stopping fry, and if you push too hard, you can directly damage the CPU.
This is why the enthusiastic motherboards often have high quality components between the CPU and the power supply-in the theory, you can give more strength to the CPU before the components fail.
Heat is one of the largest killers in this scenario, and extreme overclockers have moved to large lengths to design special cooling systems that carry more heat from the CPU and the surrounding power-distribution components as possible. Anything as far as Cryogenic fluid using, such as liquid nitrogenWhich is the most at -321F (-196), to keep things as much as possible.
If you want, you can overclock any component in a PC too much, but CPU, GPU and RAM are popular options as they can produce noticeable improvement in gaming performance.

Connected
You can overclock your monitor, but what do you need?
You were very upset with whether you can overclock your monitor or not, you did not stop thinking what you need.
Overclocking (mostly) irrelevant
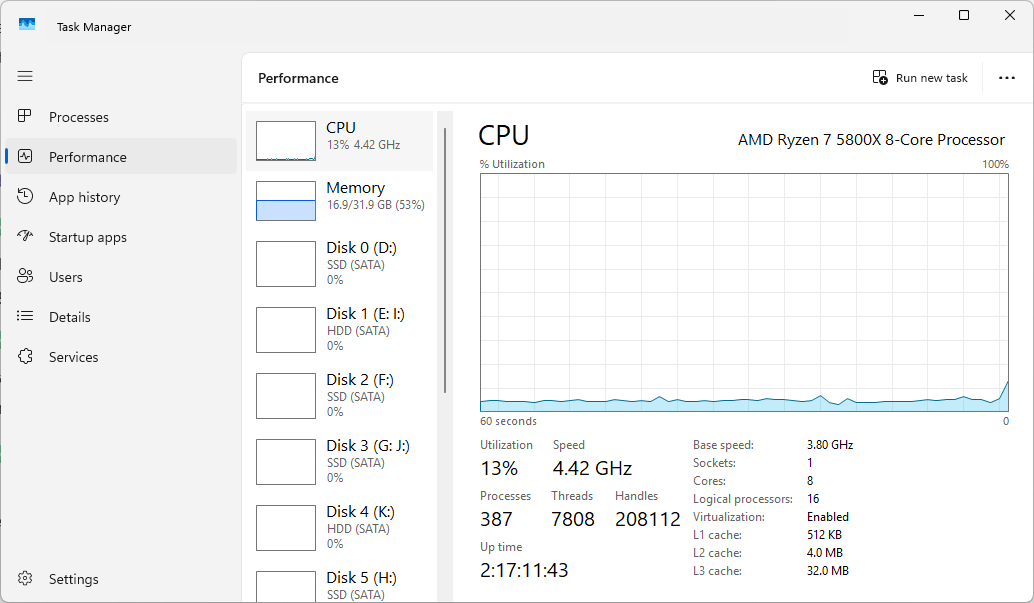
CPUS usually does not run at its maximum frequency at all times. In fact, if you open the task manager and check the performance tab, you will see that the speed of the CPU varies from moment to moment.
When you are not doing much, the CPU clock speed falls to save on electricity; When you are doing something intensive, the speed of the clock is ready to give more and more performance. This is particularly important on laptops and other mobile devices, as you have limited amounts of energy available in the battery before you need to charge.
However, modern CPUs are also able to exact the opposite by themselves.
Automatically promoting CPU frequencies
To implement that variable performance, the CPU manufacturers developed and implemented an approach, called Dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVF)Which simply changes the voltage and frequency of its CPU core.
It can also be used dramatically increase Under some circumstances your CPU clock frequency, especially when you only need a handful of core.
Separate companies do different things to CPU boosts. For example, Intel calls it “turbo boost”, and AMD calls it “the exact boost overdrive”, but the result is basically the same: When you need more performance, the CPU frequency can be extended to try automatically and to reach you.
Unlike overclocking, the promotional frequencies are not set. As soon as the demand disappears, the frequency of the CPU will fall into its general operating range. Additionally, promoting the CPU usually involves some core at just one time, while overclocking is usually applied to all of the CPU core at once.
The amount of additional heat created by promoting only a few core is limited, and it is also easy on other components related to power delivery, as you are trying to promote 2 core instead of only 16. Not necessarily there is no major loss. Most applications, especially games, cannot make full use of 8 or 16-core CPUs anyway, and promoting all the core will only give you more heat, not better.
To ensure that your CPU does not accidentally fry itself, CPU Boost Technologies also keep a limit on how fast they will set your clock speed, while with overclocking, you can do real, permanent damage if not careful.
Overclocking and boosting are not the same thing, and if you need to drive several core to their full extent, you are probably better than installing a sophisticated cooling system and overclocking your CPU. But for the average gamer, the overclocking is dead – the boosting has made it an irrelevant risk.